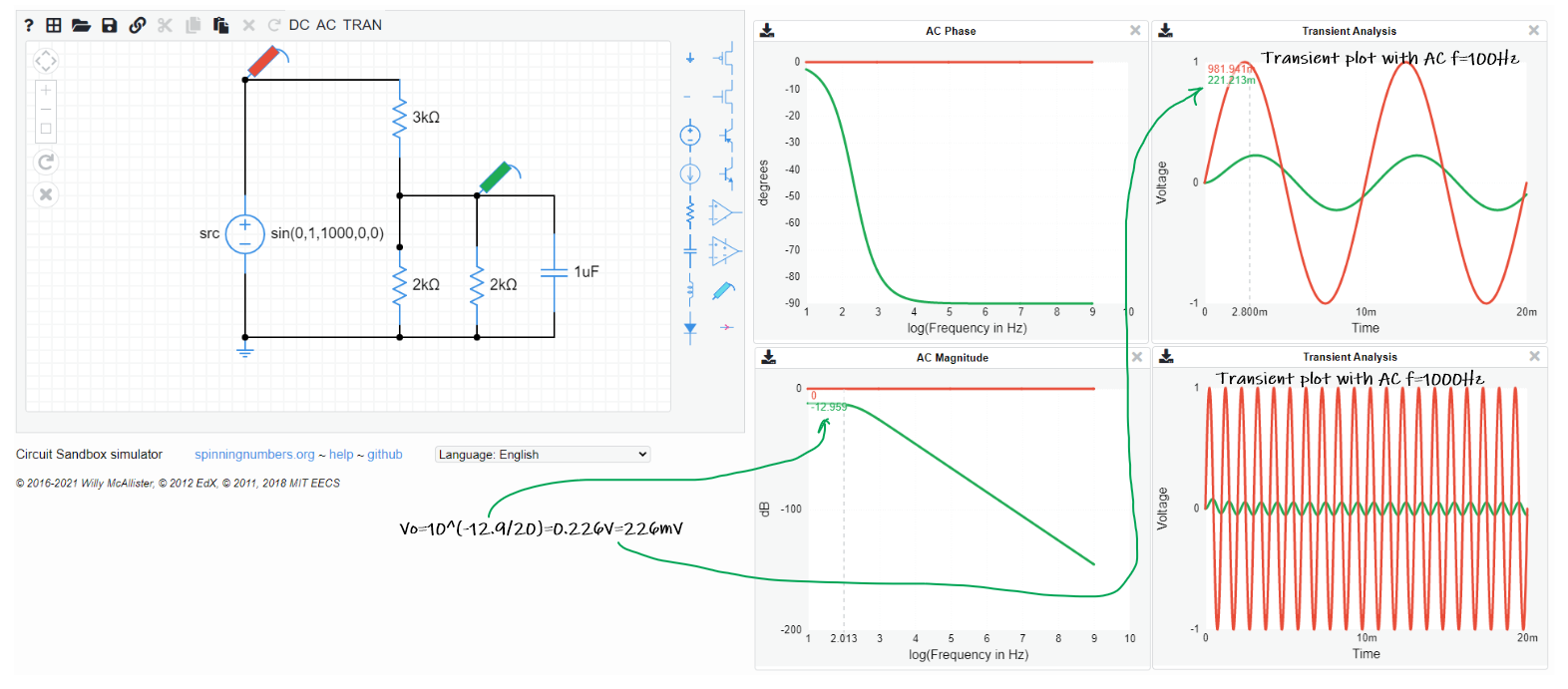
Circuits and Electronics Notes
Circuits and Electronics MITx 6.002 Notes
Last Updated: September 09, 2021 by Pepe Sandoval
Want to show support?
If you find the information in this page useful and want to show your support, you can make a donation
Use PayPal
This will help me create more stuff and fix the existent content...